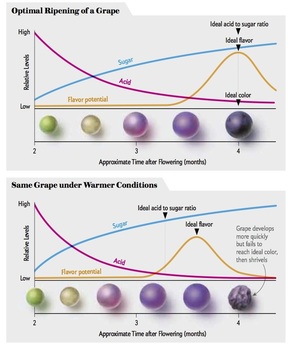
While research is ongoing to try to understand how the more than 1,000 aroma compounds identified in wine affect our flavor perception, many compounds appear to be sensitive to climate, particularly in the later stages of grape ripening. Some desirable compounds like rotundone, which gives Syrah its typical black pepper aroma, appear to accumulate more at cooler sites and in cooler years, so warmer-climate Syrahs have less of this character.  My parents' vineyard in the hills above Sonoma. My parents' vineyard in the hills above Sonoma. Winegrowers and winemakers have many options to adapt to warming climates. Growers are experimenting with new wine regions, cooler locations within existing regions (such as moving from warmer valleys to cooler hillsides), trying new varieties better suited to warmer conditions, and farming methods that provide more shade on the fruit. Winemakers can use approaches including alcohol removal and acid addition to improve wine balance. Steps like these can go a long way towards preserving great wines under climate change. Ultimately, though, there are economic and biophysical limits to this adaptation. There are also cultural limitations: the know-how and sense of place that growers cultivate along with the land over generations of family farming is not easily moved, and consumers have come to expect a distinct flavor profile from wines from their preferred regions. Great wine is grown, not made; it reflects its place of origin. If the climate changes even a little bit, local knowledge and skills that have taken generations to hone can become less relevant, even in familiar territory. But the changes we’re facing in climate are not small ones. Under our current trajectory of fossil fuel use, scientists project that the global average temperature will increase 4.7 to 8.6°F (2.6 to 4.8°C) over the next few generations. Even the low end of this range would be the difference in annual average temperatures between the winegrowing regions of Napa and Fresno today. Currently, Cabernet grapes from cooler Napa are worth more than 10 times as much as those from Fresno- a difference of over $3,000 a ton. Wine illustrates our deep reliance on nature to provide us with everything we need to live, and many of the things that make life worth living. We are in a moment of critical climate choices. Choosing to limit climate change gives us more options for a more healthy, thriving, fair, and delicious world- including more of the traditional flavors of your favorite wines.
Candice Jackson
2/1/2015 02:10:18 am
This is such a fascinating look at a potential impact of climate change. Thanks for sharing this! 5/26/2015 11:59:18 pm
Am trying to get this very message out ! Would you like to read my book: Wine and Climate Change? It is on Amazon, but I am happy to send you a pdf, Would love your comments.
Hulin Emile
8/13/2015 04:59:14 am
It's a powerful message, the global warming seems not to be take seriously as he is, a real issue at present time. Comments are closed.
|
Categories
All
Archives
November 2023
|
KIM NICHOLAS


 RSS Feed
RSS Feed

